Table of Contents
ToggleIn a world where dietary choices are as diverse as the cuisines they encompass, the distinction between vegan and vegetarian food often dances on the periphery of understanding. While both lifestyles revolve around plant-based eating, the devil is in the details—or, in this case, the ingredients. Picture this: a tantalizing spread of vibrant dishes laid out before you, each tempting your taste buds with promises of wholesome goodness. But beneath this seemingly harmonious exterior lies a culinary battleground of nuances that set vegan and vegetarian fare apart in ways both subtle and significant. From hidden animal byproducts to ethical considerations influencing every ingredient choice, exploring these seven main differences will peel back layers of complexity within these two beloved dietary paths. So buckle up and prepare for a deep dive into the delectable world of vegan versus vegetarian cuisine—it’s about to get deliciously intriguing!
Definition of Vegan and Vegetarian Food
When it comes to defining vegan and vegetarian food, the key distinction lies in the exclusion of certain ingredients. Vegan food completely avoids any animal-derived products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and even honey. This strict adherence to plant-based ingredients is a core principle of the vegan diet, driven by ethical considerations as well as health and environmental concerns.
On the other hand, vegetarian food is more flexible as it allows for the consumption of dairy and eggs while excluding meat. Vegetarians may still consume products like cheese or yogurt made from animal sources. This distinction opens up a wider range of options for vegetarians compared to vegans, providing them with additional sources of protein and nutrients.
Ultimately, choosing a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle depends on personal beliefs and health objectives. Both diets offer numerous benefits for individuals seeking a plant-based approach to nutrition while making positive contributions towards sustainability and animal welfare.

What are the Main Differences of Vegan vs. Vegetarian Food?
When comparing vegan and vegetarian diets, one of the key distinctions lies in the exclusion of animal products. While vegetarians may consume dairy products like milk, cheese, and eggs, vegans completely abstain from all animal-derived foods, including honey. This fundamental difference impacts not only dietary choices but also ethical considerations surrounding animal welfare.
Another important contrast between vegan and vegetarian food is the focus on nutritional diversity. Vegans often pay close attention to incorporating a wide variety of plant-based sources of protein, such as legumes, tofu, and quinoa, to ensure they meet their daily nutrient requirements. On the other hand, some vegetarians may rely more heavily on dairy or eggs for protein intake, potentially limiting their exploration of alternative protein-rich foods available in a plant-based diet.
Additionally, veganism tends to extend beyond just dietary preferences into a lifestyle centered on environmental sustainability and minimizing harm to animals. The ethos driving many vegans goes beyond food choices to encompass clothing options free from animal products like leather or wool and actively seeking out cruelty-free personal care items. In contrast, while some vegetarians may share similar values regarding animal rights and environmental concerns related to factory farming practices, their focus remains primarily on dietary restrictions rather than holistic lifestyle decisions.

Here are 5 Main Differences Between Vegan and Vegetarian Food
1. Ingredients of Vegan vs. Vegetarian Food
When it comes to the ingredients used in vegan and vegetarian foods, one key distinction lies in the exclusion of animal products. Vegan food strictly follows a plant-based diet, shunning all forms of animal-derived ingredients such as meat, dairy, eggs, and honey. This means that vegans rely heavily on plant-based alternatives like almond milk, tofu, tempeh, and nutritional yeast to create delicious and nutritious meals.
On the other hand, vegetarian food allows for the inclusion of some animal products, such as dairy and eggs, while excluding meat. This gives vegetarians more versatility in their ingredient choices compared to vegans. Vegetarian dishes may feature ingredients like cheese, yogurt, butter, and eggs, which can provide added richness and flavor profiles that are not typically found in vegan cuisine. It’s this flexibility that often appeals to those transitioning from a traditional omnivorous diet toward a more plant-centric lifestyle.
In essence, while both vegan and vegetarian diets center around plants as the primary source of nutrition, the inclusion or exclusion of specific animal-derived ingredients is what sets them apart in terms of culinary creativity and nutritional diversity.

Use of Animal Products in Veganism
Veganism, as a lifestyle choice aimed at minimizing harm to animals, often raises questions about the use of animal products in unexpected places. Surprisingly, even some vegan-friendly foods may contain animal-derived ingredients such as gelatin or honey. While these additions might seem minor, they present ethical dilemmas for many vegans who strive for complete adherence to their values.
However, the debate around using animal products in veganism isn’t always black-and-white. Some argue that certain animal by-products, like wool or beeswax, can be ethically sourced without causing harm to the animals involved. This gray area challenges vegans to consider the broader implications of their choices and encourages a deeper reflection on the complexities inherent in navigating a world where ethical consumption is not always straightforward.
Dairy and Eggs in Vegetarianism
Regarding vegetarianism, dairy, and eggs often play a pivotal role in the diet. While some vegetarians choose to include these animal products for their nutritional value and taste, others opt for plant-based alternatives due to ethical concerns or health reasons. Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are rich in calcium and protein, making them valuable sources of nutrients for vegetarians. Similarly, eggs are a complete protein source that can be easily incorporated into various dishes.
However, the production of dairy and eggs can raise ethical issues for some vegetarians as it involves animal agriculture practices that may not align with their values. Concerns about animal welfare and environmental sustainability have led many individuals to seek out cruelty-free alternatives such as plant-based milk or egg substitutes. By exploring these options, vegetarians can still enjoy the flavors and textures they love while supporting more ethical food choices.
2. Nutritional Content of Vegan vs. Vegetarian Food
When it comes to comparing the nutritional content of vegan and vegetarian foods, one key difference lies in the sources of protein. While both diets can provide adequate protein intake, vegetarians may have a slight edge due to the inclusion of dairy and eggs in their diet. These animal-derived products offer high-quality protein that is more easily digestible by the body, which can be beneficial for muscle growth and repair.
On the other hand, vegans must be more conscious about combining various plant-based sources to ensure they are getting all essential amino acids. This need for diversification can lead to a higher consumption of different types of food, which may provide additional nutrients such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to some lacto-ovo vegetarian diets. Additionally, vegan diets tend to be lower in saturated fats due to the exclusion of dairy and eggs, which could have positive implications for heart health over time. In conclusion, while both vegan and vegetarian diets can be nutritionally sound with proper planning, understanding these subtle differences can help individuals make informed choices that align with their health goals.

Meeting Protein Needs Differently Between Vegan and Vegetarian Food
As we explore the varying approaches to meeting protein needs through different dietary choices, one intriguing avenue is delving into plant-based sources. While both vegan and vegetarian diets emphasize the importance of plant proteins, vegans often rely solely on plants to meet their requirements. This leads them to explore a wider array of options, such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and soy products like tofu.
On the other hand, vegetarians may incorporate dairy and eggs into their diets to enhance protein intake. This distinct approach offers them versatility in their meal planning while also reaping the benefits of these animal-derived protein sources. By understanding how each diet uniquely tackles protein requirements, individuals can make informed choices that align with their nutritional goals and values. Ultimately, embracing these differences sheds light on innovative ways to meet protein needs without compromising on taste or variety in plant-based cuisine.
3. Ethics and Philosophy of Vegan vs. Vegetarian Food
The ethics and philosophy behind choosing either vegan or vegetarian food delve deep into our relationship with the environment, animals, and personal health. While both diets prioritize plant-based foods, vegans take a more stringent approach by excluding all animal products, including dairy and eggs. This stems from the belief that consuming any animal-derived products still contributes to animal exploitation and suffering.
On the other hand, vegetarians may argue that their diet choices reflect a balanced compromise between ethical values and personal preferences. They often cite concerns about sustainability and ethical treatment of animals in their decision to avoid meat while still allowing for some consumption of dairy and eggs. The philosophical debate surrounding these dietary choices is complex, highlighting the interconnectedness of ethics, health, and environmental impact in food production.

Animal Exploitation Views in Vegan and Vegetarian Food
Animal exploitation is a contentious issue that lies at the heart of debates surrounding vegan and vegetarian diets. While both diets aim to reduce harm to animals, the views on animal exploitation can differ significantly. Vegans typically take a more stringent stance against all forms of animal exploitation, including those in the agriculture, entertainment, and clothing industries. They argue that any form of use or consumption of animal products perpetuates cruelty and violence towards sentient beings.
On the other hand, some vegetarians may hold more nuanced views on animal exploitation, permitting certain forms of use, such as dairy and egg production, while condemning practices like factory farming. This discrepancy often sparks intense discussions within the plant-based community about where to draw the line between ethical consumption and exploitation. The evolving attitudes towards animal rights continue to shape dietary choices and how individuals navigate their values with their culinary preferences.
4. Culinary Diversity of Vegan vs. Vegetarian Food
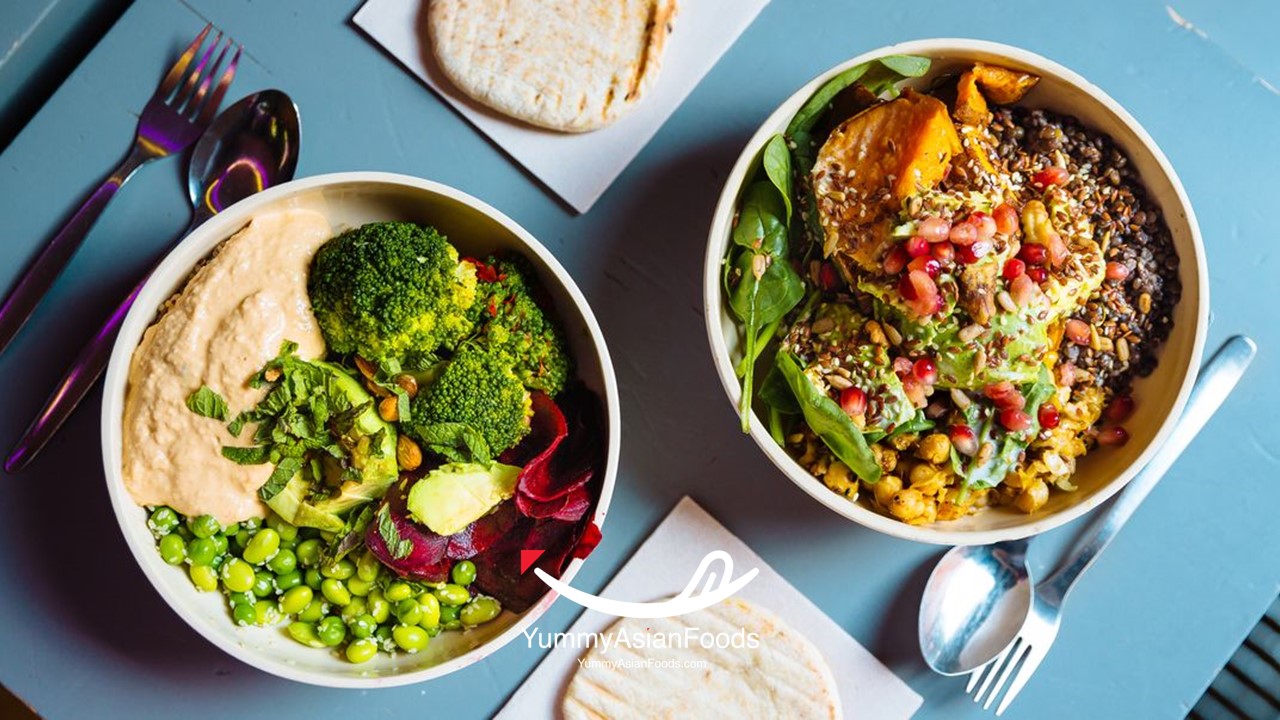
When it comes to culinary diversity, both vegan and vegetarian food offer a wide array of flavorful options that cater to various tastes and preferences. Vegetarian cuisine often revolves around incorporating dairy products like cheese and milk into recipes, adding rich textures and creamy flavors that can enhance dishes such as pasta, salads, and sandwiches. On the other hand, vegan cooking focuses on plant-based ingredients like tofu, tempeh, legumes, and nuts to create savory meals that are not only delicious but also packed with nutrients.
The distinct flavor profiles of vegan dishes stem from the innovative use of herbs, spices, sauces, and creative cooking techniques that showcase the natural flavors of vegetables and grains without relying on animal-derived ingredients. In comparison, vegetarian cooking might incorporate more traditional seasonings and preparations due to the inclusion of dairy products. Both culinary styles excel at creating diverse menus ranging from hearty soups and stews to refreshing salads and vibrant stir-fries, each offering a unique gastronomic experience that celebrates the abundance of wholesome plant-based foods available for exploration in the kitchen.

Range of Vegan Substitutes vs. Vegetarian Food Options
When it comes to exploring the world of plant-based diets, the range of vegan substitutes often outshines vegetarian options in terms of creativity and variety. Vegan alternatives have pushed culinary boundaries with innovative products like plant-based meats, dairy-free cheeses, and egg substitutes that closely mimic their animal-derived counterparts. This diversity allows vegans to enjoy a wide spectrum of dishes without sacrificing taste or texture.
On the other hand, while vegetarian food options may not offer as extensive a selection of substitutes, they excel at highlighting the natural flavors and textures of whole foods. Vegetarian dishes showcase the beauty of vegetables, grains, legumes, and dairy products in their purest forms without relying heavily on processed alternatives. This emphasis on simplicity and authenticity adds a unique charm to vegetarian cuisine that resonates with those seeking a closer connection to nature through their diets.
5. Environmental impact of Vegan and Vegetarian Food
It’s no secret that plant-based diets have been gaining popularity in recent years due to their perceived environmental benefits. Vegan and vegetarian food options are often touted as more sustainable alternatives to meat-heavy diets, with claims of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land degradation. But how significant is the impact of these dietary choices on the environment?
Recent studies suggest that while vegan and vegetarian diets generally have a lower environmental footprint compared to meat-based diets, the actual impact can vary depending on factors such as food production methods and transportation distances. For example, monoculture farming practices used to produce some vegan staples like soy and almonds can lead to soil degradation and biodiversity loss.
In addition, the carbon footprint of certain plant-based foods may not be as low as initially thought when considering factors like processing methods and packaging waste. It’s clear that while transitioning to a vegan or vegetarian diet can have positive environmental implications, it’s essential to consider the broader picture of sustainability behind each food choice.

Sustainability Factors in Vegan vs. Vegetarian Food Choices
When exploring the sustainability factors in vegan versus vegetarian food choices, it becomes evident that the environmental impact of these dietary preferences differs significantly. Vegan diets, which exclude all animal products, have been touted as more sustainable due to their reduced carbon footprint and water usage compared to vegetarian diets. This is mainly because the production of dairy and other animal-derived foods typically requires more resources, contributing to deforestation and higher rates of greenhouse gas emissions.
However, it’s important to note that not all plant-based foods are created equal when assessing sustainability. For example, certain crops like avocados or almonds can have a heavier environmental impact due to factors such as water consumption and intensive farming practices. Therefore, individuals opting for either a vegan or vegetarian diet should also consider sourcing their food from local and organic sources to enhance the sustainability of their food choices.
In essence, while both veganism and vegetarianism offer tangible benefits in terms of sustainability compared to omnivorous diets, the nuances lie in understanding the broader implications of our food choices. By taking a holistic approach that considers not just what we eat but how it is produced and sourced, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their ethical values while minimizing environmental harm for a truly sustainable future.
6. Health Effects of Vegan and Vegetarian Food
Adopting a plant-based diet, whether vegan or vegetarian, can have profound effects on your health. Studies have shown that both diets are associated with lower rates of heart disease, high blood pressure, and certain types of cancer. Vegan diets, which exclude all animal products, including dairy and eggs, tend to be higher in fiber and lower in saturated fats compared to vegetarian diets. This difference often translates into better weight management and a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Furthermore, the abundance of antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables commonly consumed by vegans and vegetarians can boost immune function and promote overall well-being. Plant-based diets are also linked to improved digestion due to their rich fiber content. By eliminating processed foods and focusing on whole, nutrient-dense plant foods, individuals following these diets may experience increased energy levels and improved mental clarity. Ultimately, choosing between veganism or vegetarianism can lead to a range of health benefits that support long-term vitality.

Comparing Health Benefits and Potential Risks Between Vegan and Vegetarian Food
When it comes to comparing the health benefits and potential risks of vegan and vegetarian diets, it’s important to consider nutrient intake. Vegans typically have lower intakes of certain nutrients, like vitamin B12, which is primarily found in animal products. On the other hand, vegetarians may still consume dairy and eggs, helping to bridge some nutritional gaps.
In terms of health benefits, both vegan and vegetarian food consumers are associated with lower rates of heart disease, high blood pressure, and obesity. However, vegans tend to have a lower risk of certain chronic illnesses due to their exclusion of all animal products. It’s crucial for individuals following either diet to ensure they are meeting their nutrient needs through proper planning and possibly supplementation.
Overall, both vegan and vegetarian diets offer numerous health advantages while also presenting potential risks if not properly balanced. Understanding the differences between these two plant-based diets can help individuals make informed choices that align with their health goals and preferences. Remember, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to nutrition!
Vegan or Vegetarian Food: Which is Better?
While both vegan and vegetarian diets have their own merits, the debate over which is better often leads to passionate discussions among individuals advocating for either lifestyle. Vegans exclude all animal products from their diet, including dairy and eggs, while vegetarians may choose to consume these animal-derived products. One key difference between the two is the ethical standpoint: vegans typically avoid all animal exploitation, while vegetarians may still support industries like dairy farming.
From a health perspective, both diets can be nutritious if well-balanced. However, vegans may need to pay closer attention to certain nutrients, like vitamin B12 and iron, that are more readily available in animal products. On the other hand, some argue that a vegetarian diet provides more flexibility and potentially easier adherence due to the inclusion of dairy and eggs as protein sources. Ultimately, the choice between vegan or vegetarian food comes down to individual beliefs, nutritional needs, and personal preferences in terms of ethics and sustainability.

How To Choose Between Vegan or Vegetarian Food
When deciding between vegan or vegetarian food, it’s important to consider your personal values and health goals. Vegans avoid all animal products, including dairy and eggs, while vegetarians may include these in their diet. If you’re passionate about animal welfare and reducing environmental impact, opting for a vegan diet might align better with your beliefs. On the other hand, if health benefits are your primary concern, a well-balanced vegetarian diet can provide essential nutrients that may be harder to obtain through a strictly vegan approach.
Moreover, exploring the culinary diversity of both diets can be an exciting journey that opens up new flavors and cooking techniques. By experimenting with plant-based ingredients like lentils, tofu, and beans in vegan dishes or incorporating dairy products into vegetarian meals, you can create delicious and satisfying meals that cater to your tastes and preferences. Ultimately, whether you choose to go vegan or vegetarian depends on understanding what resonates most with you personally, be it ethical considerations or nutritional requirements – as both dietary choices offer unique benefits worth exploring.

Why Should You Shift to Vegan or Vegetarian Food if You Are a Meat Lover?
If you’re a die-hard meat lover, the idea of switching to vegan or vegetarian food might seem daunting. However, making this shift can introduce you to a whole new world of flavors and textures that you never knew existed. Plant-based dishes are incredibly diverse and can offer a wide variety of tastes that can rival any meat-based meal.
Choosing vegan or vegetarian options also comes with various health benefits. These diets are typically lower in saturated fats and cholesterol, which can help reduce your risk of heart disease and other health conditions. Additionally, plant-based foods are rich in essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that are vital for your overall well-being.
By transitioning to vegan or vegetarian food as a meat lover, you have the opportunity to explore innovative cooking techniques and ingredients that can transform your culinary experience. Embracing this change not only benefits your health but also allows you to contribute positively to animal welfare and environmental sustainability. Making this switch opens up a world of delicious possibilities that can surprise even the most dedicated carnivores.

Parting Thoughts: Choosing Between Vegan and Vegetarian Food Impacts Lifestyle, Environment, and Ethics
Ultimately, the choice between vegan and vegetarian food extends beyond individual dietary preferences; it serves as a powerful catalyst that can influence various aspects of our lives. By opting for one diet over the other, individuals inadvertently make an impact on lifestyle, environmental sustainability, and ethical considerations. Choosing a vegan lifestyle signifies a commitment not just to personal health but also to global issues such as reducing carbon footprints and animal cruelty. On the other hand, opting for a vegetarian diet emphasizes a different set of values centered around sustainability and conscious consumption.
Moreover, understanding the key differences between vegan and vegetarian diets allows individuals to align their choices more closely with their personal beliefs and principles. For some, this decision stems from environmental concerns about industrial livestock farming practices; for others, it may be rooted in ethical considerations related to animal welfare. It is through this critical awareness that we can truly appreciate the far-reaching implications of our dietary decisions on both our immediate surroundings and the wider global community. In essence, choosing between vegan and vegetarian food goes beyond mere meal planning—it embodies a holistic approach toward mindful living that reverberates across various spheres of life.